- Partners trialed non-real time RAN Intelligent Controller (Non-RT RIC) technology based on O-RAN specifications
- The Non-RT RIC brings intelligence and programmability to RAN by enabling third-party applications (rApps) to manage and optimize radio resources
- Multi-vendor collaboration assessed integration complexity of the Non-RT RIC, rApps and Service Management and Orchestration (SMO) framework – and summarized in whitepaper.

Deutsche Telekom today underlined its ongoing commitment to the development of Open RAN technology, by announcing details of a multi-vendor trial around programmable radio access networks that demonstrates the potential of the Non-RT RIC and rApp concept to automate and optimize disaggregated RAN.
The Non-RT RIC brings intelligence, agility, and programmability to disaggregated radio access networks and enables third-party applications (rApps) that can perform closed-loop automation and optimization of RAN elements and resources. However, the multi-vendor integration of Non-RT RIC, rApps and SMO also introduces challenges that must be addressed.
Working together with AirHop, Juniper Networks, VIAVI Solutions and VMware, the partners completed a RAN closed-loop optimization Proof of Concept (PoC) within Deutsche Telekom’s lab environment in a multi-vendor setup based on ONAP & O-RAN specifications. Closed loop rApp algorithms were onboarded and deployed on partners’ Non-RT RIC. During the PoC, partners successfully executed two use cases:
- Physical Cell Identifier (PCI) optimization focused on detection and resolution of PCI confusion and collision scenarios.
- Energy Savings dynamic Multi-Carrier management (ESMC) using an Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning (AI/ML) model, trained to determine the optimum time to enable/disable sleep-mode on capacity cells in order to save energy while maintaining user quality of experience (QoE).
Initial tests were performed in a real end-to-end lab setup using a small O-RAN network to validate end-to-end configuration and performance management (CM & PM) integration for a real network environment. Most tests were executed on a more complex network setup using an O1 network emulator (RIC tester) to validate rApp logic and stress test the RIC components to benchmark the various solutions.
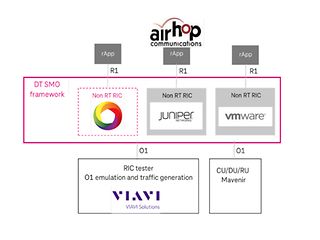
About the setup
- Deutsche Telekom provided a self-developed SMO framework along with a Non-RT RIC solution based on the O-RAN SC Non-RT RIC
- Juniper Networks and VMware integrated their Non-RT RIC products into DT’s SMO framework
- AirHop integrated two rApps for PCI optimization and ESMC with each Non-RT RIC
- VIAVI provided their RIC tester to emulate the O1 interface
The multi-vendor framework presents integration challenges. However, this PoC has shown from a high-level perspective that the adoption of the SMO, Non-RT RIC and rApp framework is promising in how it allows for the decoupling of optimization algorithm development, the supporting platform development and the system integration – so that components from different parties can form a truly disaggregated RAN optimization concept.
“With this PoC, we set out to assess the technical integration complexity of the components delivered by each party, the level of customization required, to gauge the maturity of products and to identify potential future standardization requirements,” stated Petr Ledl, VP, Head of Network Trials and Integration Lab, Deutsche Telekom.
A detailed outline of these challenges, as well as customizations and future standardization requirements, plus areas of further focus, are detailed in the trial White Paper (pdf, 1.2 MB).
“At DT our primary focus is always on driving innovation to support the best customer experience. The RIC and rApps are key to programmability, automation, and optimization in radio access networks. Taking the learnings from this successful trial, we will now continue the work with our ecosystem partners to accelerate Non-RT RIC/rApp development towards production readiness”, added Petr Ledl.
RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC) and Apps
A RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC) is a software-defined component of the Open RAN architecture that’s responsible for controlling and optimizing RAN functions behavior. The RIC enables fast onboarding of third-party applications (Apps) that automate and optimize RAN operations at scale. It also supports innovative use cases while providing lower introduction time and ultimately lower total cost of ownership (TCO) of mobile operators as well as enhancements to customers’ quality of experience (QoE).
The non-real-time RIC (Non-RT RIC) is part of the Service Management and Orchestration (SMO) framework, centrally deployed in the service provider network. It enables greater-than-one-second control and policy guidance over the RAN elements and their resources through so called rApps.
It also enables AI/ML capabilities for the RAN and uses long-term network data, such as performance metrics as well as enrichment data from external applications to train and generate AI/ML-driven applications.






